At heart, the search engine’s role is to:
- Understand the world’s knowledge and
- Match it to user needs
- Instantly
The technology that powers the Search Engine has changed many thousand of times over, but the core philosophy established by that first handful of visionaries and reinforced by Google in particular – remained intact. Thus, the best way to define SEO is by reverse-engineering how any given website feeds these 3 aspects of a search engine.
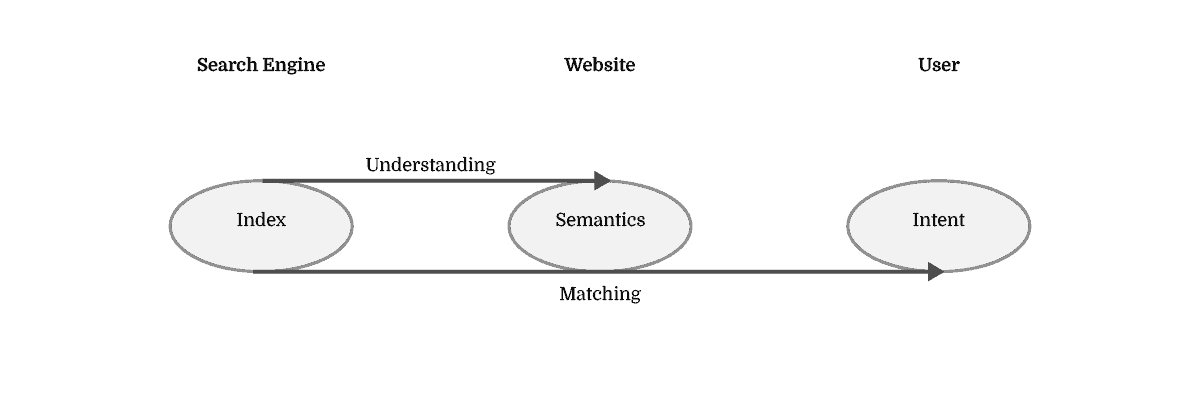
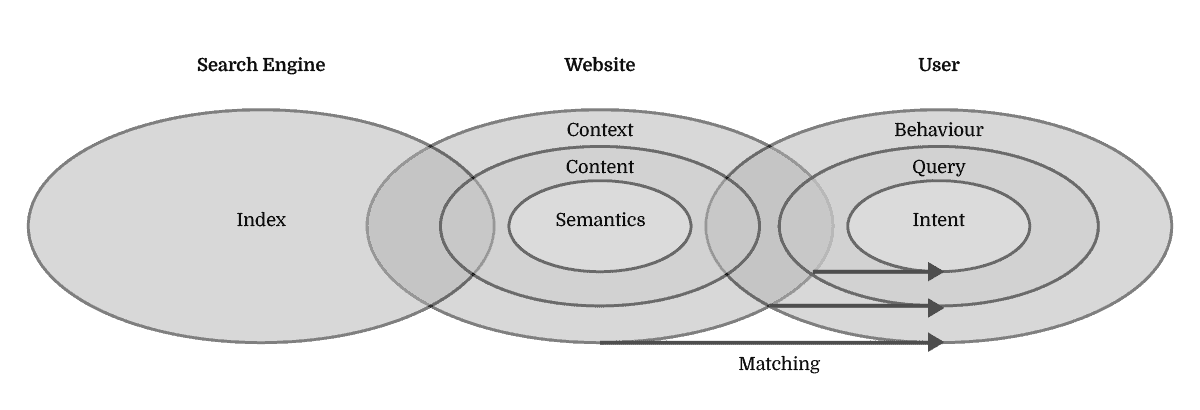
The Query Fulfilment is the single mission of any given search. The Search Engine goes to great lengths at estimating the ranking of the most relevant resources for fulfilling that query. However, the website has the absolute power in determining whether that query will, in fact, end up being fulfilled. In an imperfect world, in order to understand knowledge, search engines look at website content and match it to user needs through search queries leading to Search Engine Results Pages.
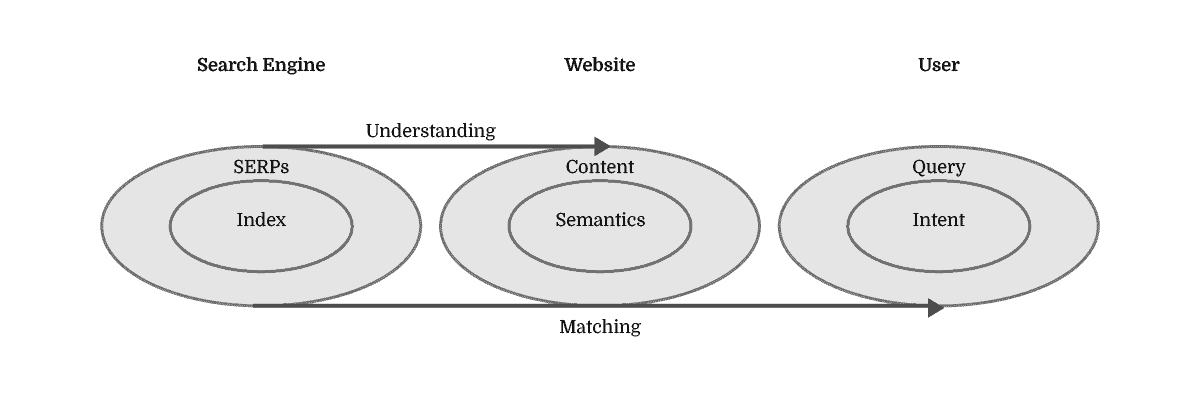
Understanding the world’s knowledge and matching it to user needs is a task difficult enough, but it becomes even more so when both aspects are constantly changing. Search Engine Algorithm Updates are designed to either increase the search engine’s depth of knowledge or accuracy of matching it to user needs by getting a tighter grip on context and user behaviour.
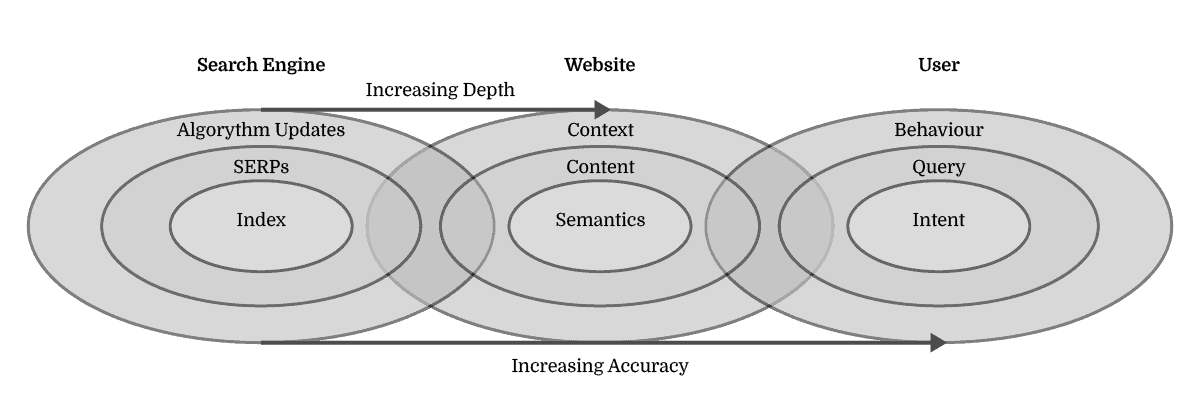
Algorithm updates that aim to primarily increase the search engine’s depth of understanding of information are looking at website’s context and content, in order to get a better grasp on semantics.
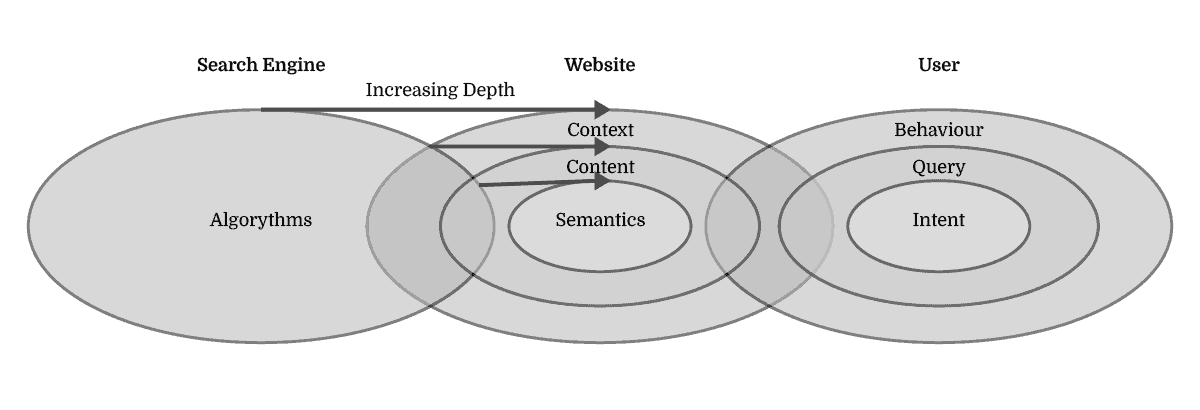
Algorithm updates that aim to primarily increase the accuracy of matching knowledge to user needs are looking at User Behaviour and Search Queries in order to anticipate Search Intent.
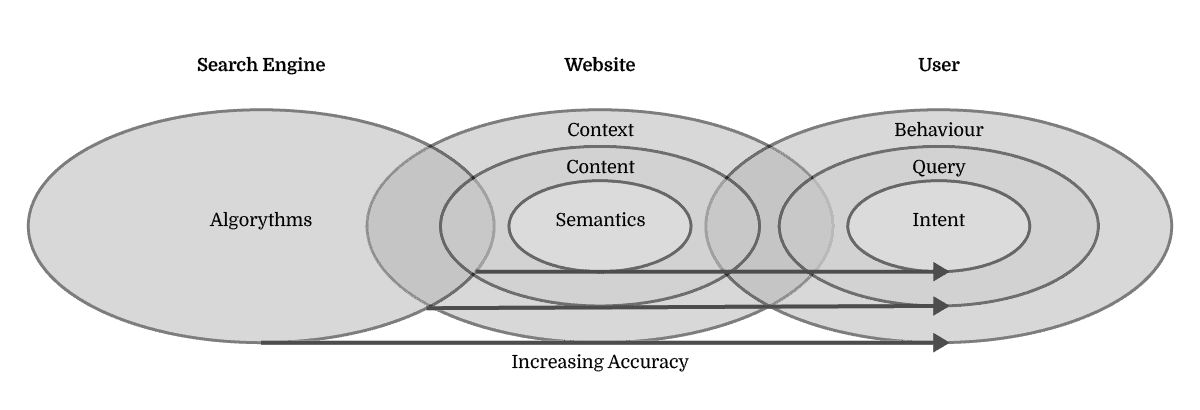
So, if we reverse this vision of a search engine to define the scope of SEO, we obtain the practice of understanding your customers in increasing depth in order to serve their knowledge needs with increasing accuracy. Thus, the role of the website is first and foremost to understand its user in order to serve the right semantics by investigating their search-behaviour, search-queries and search-intent.
Secondly, it’s about actuating the website’s wider context, content and semantics in a manner that allows fulfilling user queries and intent with increasing accuracy over time to drive their behaviour.
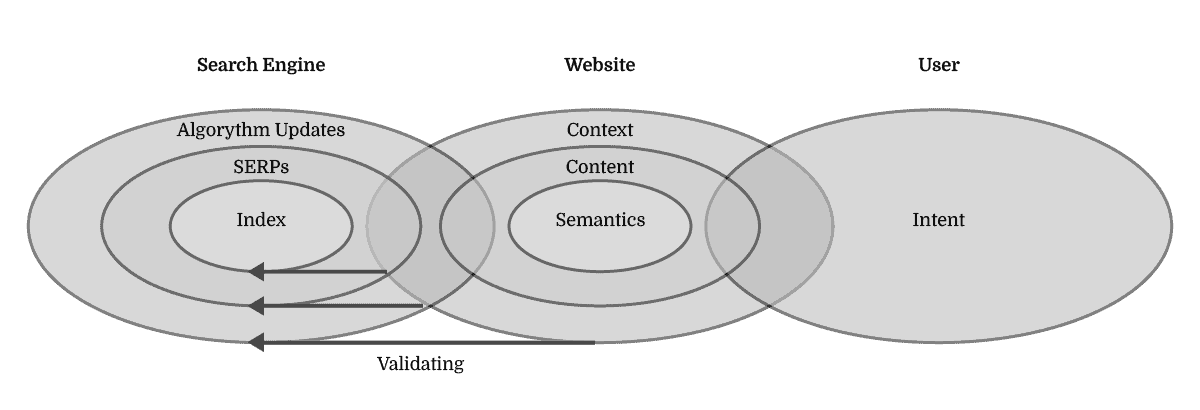
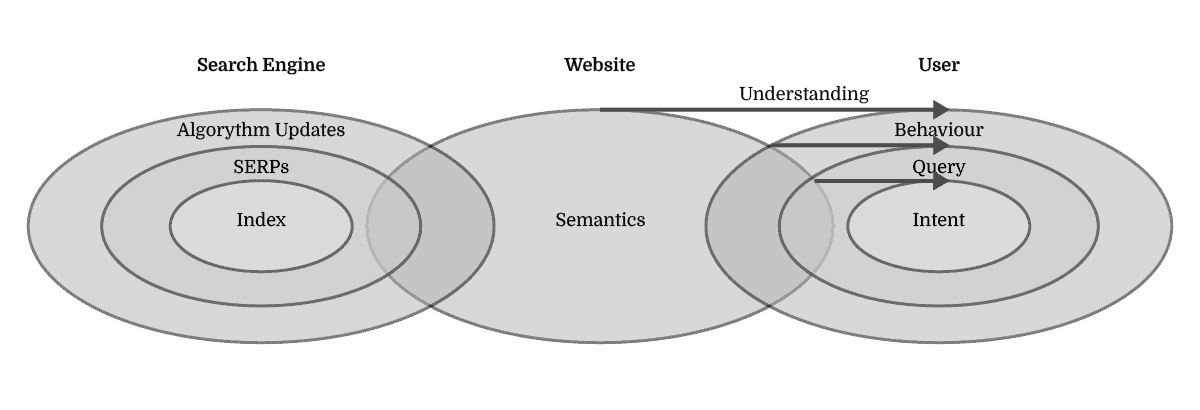
Lastly, it’s about recognising that the rankings, SERPs, and algorithm updates are merely a delayed validation of past SEO efforts as opposed to a practical guide to setting the optimisation needs.